Australia is known for having an abundance of natural resources, such as coal, natural gas, and uranium. These resources have supported the nation’s economy and energy requirements for decades, making it one of the biggest exporters of fossil fuels globally. Australia has recently been under increased pressure to switch to more ecologically friendly and renewable energy sources. Our country is currently at a crossroads where the choices taken today will significantly influence the future of its energy sector and environment because of the implications of climate change and the need to cut greenhouse gas emissions. But how much clean energy does Australia use? Get to know all about it right in this article.
Australia's Current Energy Strategy
Australia’s current energy strategy is focused on ensuring the country has a reliable, affordable, and sustainable energy system that can meet the needs of the community and support economic growth. The strategy is guided by the National Energy Security Assessment (NESA) and the National Energy Productivity Plan, which set out the framework for energy policy and investment in the country.
One of the key elements of Australia’s energy strategy is the promotion of renewable energy sources.
The country has set a target of achieving 50% renewable energy by 2030, and this target is supported by various state and territory-level renewable energy targets.
To achieve this target, the government has implemented a range of policies and initiatives, including the Renewable Energy Target (RET)
The government is also investing in energy storage technologies to support the integration of renewable energy sources into the electricity grid. This includes the development of large-scale battery storage projects, such as the 150 MW Hornsdale Power Reserve in South Australia.
Overall, Australia’s current energy strategy is focused on achieving a balanced and sustainable energy mix that can meet the country’s energy needs while reducing its environmental impact. The government is committed to investing in renewable energy and improving energy efficiency while ensuring traditional energy sources continue to be available and affordable.

Solar Energy is a Growing Part of the Australian Government’s Energy Mix
According to the Clean Energy Australia Report 2021, solar energy is now the fastest-growing renewable energy source in the country. In 2021, the total installed capacity of solar power in Australia has reached 27.6 GW, an increase of 46% compared to the previous year. This capacity is expected to grow, with the report predicting that Australia will generate 69% of main grid energy from all renewable energy sources combined.
The growth in solar power has been driven by a combination of factors, including falling costs, improved technology, and government rebates. The Australian government has put in place a number of policies and programs to support the growth of solar energy, such as the Small-scale Renewable Energy Scheme and the Renewable Energy Target, which provides opportunities for the deployment of small-scale renewable energy projects and small-scale solar systems on homes and businesses, respectively.
In addition to government support, the growth in solar power has been driven by private investment, particularly in large-scale solar projects. As of 2023, there are several large-scale solar projects underway in Australia
Overall, solar energy is now a significant and growing part of Australia’s energy mix. It is expected to play an important role in the country’s transition to a more sustainable energy system.
How Much Clean Energy Does Australia Use?
As of 2021, renewable energy sources account for around 32.5% of Australia’s total electricity generation capacity, according to the Clean Energy Australia Report 2021. This includes sources such as wind, solar, hydro, and bioenergy. Of these sources, solar energy is currently one of the largest contributors, accounting for around 12.1% of the total electricity generation capacity, followed by wind energy at around 11.7%.
Wind power is another significant contributor to Australia’s renewable energy mix. The country has some of the world’s best wind resources, particularly in South Australia, Victoria, and Tasmania. As of 2021, there are 102 wind farms in Australia, with a total capacity of over 26,804 GWH.
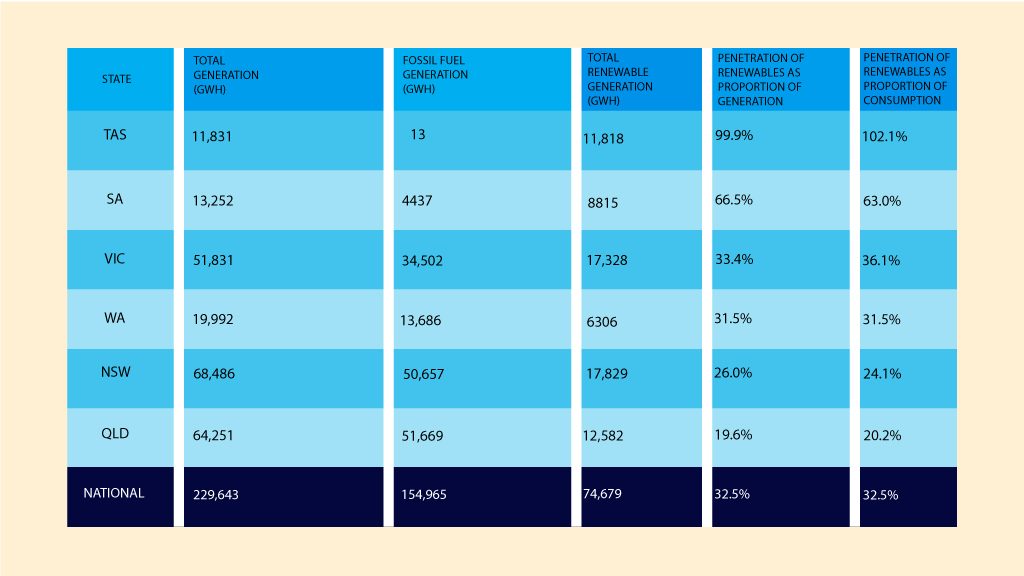
Hydropower is also an important source of renewable energy in Australia, although its contribution is relatively small compared to solar and wind. There are around 100 small and large hydropower plants across the country, with a total capacity of around 16,128 GWH.
Bioenergy and geothermal energy are two other renewable energy sources that contribute to Australia’s energy mix. Bioenergy is produced from organic matter such as wood waste, sugarcane bagasse, and landfill gas. Geothermal energy is produced from the heat of the earth’s core. While these sources are not as widely used as solar and wind power, they still play a role in Australia’s renewable energy mix.
In recent years, there has been a significant increase in renewable energy investment in Australia. The country has set a target of achieving 50% renewable energy by 2030, and many states and territories have set even more ambitious targets. For example, South Australia aims to achieve 100% renewable energy by 2030, while the Australian Capital Territory has already achieved this target.







