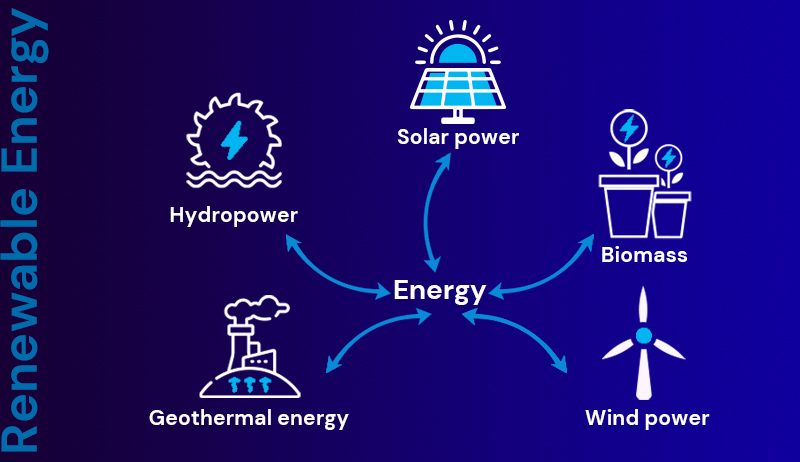
Renewable energy comes from different sources, such as solar and wind power. It’s often called “clean energy” because it produces little or no carbon emissions. It’s also called “green energy” because it comes from natural sources.
With a focus on sustainability nowadays, new technologies are used to include renewable energy in sustainable building design. People can use clean energy at home by installing systems to produce electricity or using renewable sources to heat and cool water and spaces.
Understanding Sustainable Building Design
Sustainable building design means creating buildings that are good for the environment and using resources wisely. These buildings are designed to use less energy and water, reduce waste, and minimize natural harm.
Sustainable buildings also aim to be healthier for the people who live or work in them by using safe and environmentally friendly materials. They often use renewable energy, like solar power, and are built to last a long time with minimal environmental impact.
The goal is to create structures that have a smaller impact on the environment and promote healthier living spaces for people. This means thinking carefully about how buildings are made, how they function, and how they affect their surroundings over time.
Here are some primary factors that come with sustainable building design:
Energy Efficiency: Sustainable buildings use less energy by incorporating better insulation, energy-efficient windows, and systems that control heating, cooling, and lighting. They also typically rely on renewable energy sources like solar panels or wind power.
Water Conservation: These buildings are designed to use water wisely, with low-flow taps, rainwater collection systems, and efficient landscaping irrigation.
Environmentally Friendly Materials: Sustainable buildings use non-toxic, recyclable materials with a low environmental impact. These materials can include recycled materials or those sourced from sustainable forests.
Waste Reduction: Sustainable buildings aim to minimize waste during construction by using materials efficiently and recycling leftovers. Once built, they are designed to reduce ongoing waste by incorporating recycling systems and composting options.
Healthy Living Environment: Sustainable design also focuses on creating a healthier indoor environment by improving air quality, using natural light, and avoiding materials that emit harmful chemicals.
Long-Term Durability: These buildings are made to last, requiring less maintenance and repairs over time, reducing their environmental impact.
Overall, sustainable building design involves smart choices that benefit people and the planet. It ensures that the building is eco-friendly, energy-efficient, and comfortable to live or work in.
Sustainable Building Design Strategies and Goals

Using sustainable design has many advantages, such as saving money, improving comfort, and making buildings more enjoyable.
Here are some common strategies used in sustainable buildings:
- Passive Sustainable Design: This includes natural light, good airflow, and using materials that store heat to make the building more energy-efficient.
- Active Sustainable Design: This involves using energy-efficient systems for heating, cooling, lighting, and hot water usage.
- Renewable Energy: Sustainable buildings often use natural energy sources, like solar and wind, to power the building.
The main goal of these strategies is to reduce the building’s impact on the environment while creating a functional and attractive space. Some specific goals for sustainable building design include:
- Net Zero Building: A building that generates as much energy as it uses over a year.
- Carbon Neutral Building: A building that doesn’t use fossil fuels or release greenhouse gases.
- Living Buildings: These buildings produce their energy, collect and clean water, use only non-toxic, renewable materials, and are designed to improve people’s well-being while supporting fairness and equality.
Renewable Energy Integration for Sustainable Building Design| The Role of Renewable Energy in Sustainable Building Design
Incorporating renewable energy sources such as solar and wind into sustainable building design is a critical step toward green buildings and environmental preservation in an era when sustainability is a requirement rather than an option.
Integrating solar, wind, and geothermal technologies into urban landscapes fosters a sustainable relationship with the environment.
It propels the architectural industry toward a future where buildings serve as innovative and efficient ecosystems rather than mere physical structures.
Solar Energy: Photovoltaics and Thermal| The Role of Solar Panels in Sustainable Architecture
Solar energy can be turned into electricity using silicon photovoltaic (PV) panels. These panels come in three main types: monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin film. They can be installed on the roofs or walls of buildings.
In 2023, global solar energy capacity grew by nearly 50%, especially due to China’s rapid installation of solar panels. This shows how fast the technology advances and how easily it can be used in modern buildings.
Solar Thermal Energy:
Solar thermal systems use sunlight to produce heat, often to heat water. The system collects sunlight, concentrates it, and transfers the heat to a liquid, which can create steam.
This steam drives a turbine connected to a generator, producing electricity. Solar thermal technology is especially useful for large-scale operations like factories and district heating systems, as it is very efficient for heating in big setups.
Wind Energy| Integrating Wind Turbines into Building Design
Wind turbines turn the energy of moving air into electricity. The Bahrain World Trade Centre was the first skyscraper to use wind energy in its design.
Modern advancements include vertical-axis turbines, which work well in cities because they don’t need to face the wind and can fit into smaller spaces.
Large turbines can meet a significant part of a building’s energy needs, with some even providing power for thousands of homes yearly.
By the end of 2023, global wind energy capacity had grown by 9%, reaching over 906 gigawatts, showing rapid advancements and increased use in rural and urban areas.
Types of Wind Turbines:
- Horizontal-axis wind Turbines (HAWTs)
- Vertical-Axis Wind Turbines (VAWTs)
Smaller wind turbines can be placed on rooftops or built into a building’s structure, providing a direct renewable energy source. This is effective in cities with limited space, but wind is available.
In areas with enough wind, buildings can meet most of their energy needs with nearby freestanding turbines. These setups can range from small community wind projects to large wind farms that send power to the grid.
Geothermal Energy| How to Integrate Geothermal Systems into Building Design?
Geothermal systems heat and cool using the stable temperature beneath the earth’s surface. Geothermal heat pumps (GHPs) transfer heat to and from the ground through a heat exchanger, making them very efficient and less affected by outdoor temperatures.
These systems can be set up in different ways depending on land space and soil conditions, such as horizontal, vertical, or pond/lake setups.
Types of Geothermal Systems:
- Horizontal Systems
- Vertical Systems
- Pond/Lake Systems
Careful planning is needed to integrate geothermal systems into buildings.
Here’s a simple process:
Site Assessment: Before installation, the site must be evaluated. This includes checking the soil and rock type, groundwater presence, and land availability to decide if a horizontal, vertical, or pond/lake system will work best.
Designing the Ground Heat Exchanger: The system uses a network of pipes underground (or in water) to transfer heat. The setup can be horizontal or vertical or placed in nearby water bodies.
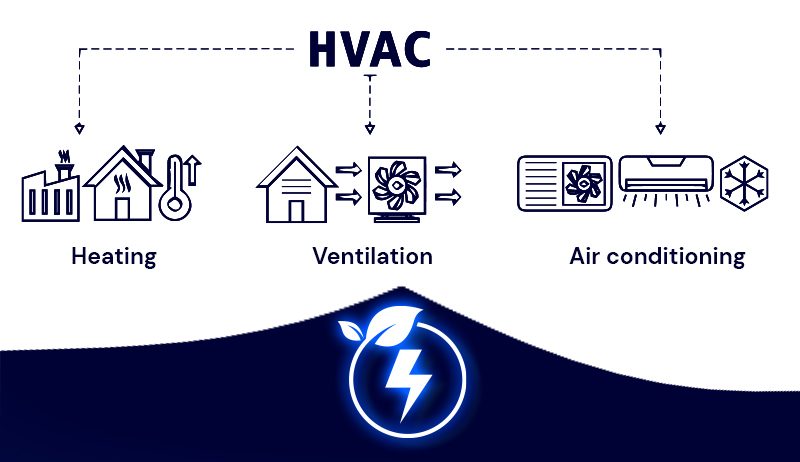
Connecting to Building Systems: The geothermal system must be connected to the building’s heating and cooling system (HVAC). It can distribute heated or cooled air or water through ductwork or radiant floors.
Energy Management System (EMS) Integration: An EMS can control the geothermal system to run during low-energy times to save costs. It also monitors the system’s performance to ensure it operates efficiently.
How to Construct Sustainable and Energy-efficient Buildings? Sustainable Building Design Principles
Due to climate change, building in an environmentally friendly and energy-efficient way is more important than ever.
Here’s a simple guide on how to create sustainable buildings, from using renewable energy and sustainable materials to improving indoor air quality.
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is key to reducing the energy a building needs and lowering its environmental impact.
This can be achieved using energy-efficient appliances, lighting, and automated doors, which help save energy by minimizing heat loss or gain. These measures lower energy use and reduce operating costs.
Renewable Energy
Sustainable Materials
Using eco-friendly materials is a crucial part of sustainable construction. Materials like reclaimed wood, recycled steel, and natural insulation like hemp or cotton reduce the building’s environmental impact.
These materials are better for the planet and cost-effective over time, as they often require less maintenance and reduce long-term expenses.
Indoor Air Quality
Good indoor air quality is essential for the health of the people inside a building. Using low-VOC (volatile organic compounds) paints, sealants, and adhesives prevents harmful chemicals from polluting the air.
Installing air purification systems further improves air quality by removing allergens and pollutants. Automatic doors can also help by controlling airflow, regulating temperature, and keeping outdoor pollutants out.
Building sustainable, energy-efficient structures is a crucial way to combat climate change. A complete approach, covering everything from design and construction to operation and maintenance, is needed.
Contact Cyanergy for more informative content like this. Or talk to an expert!







