In business, the urgency of addressing climate change and its associated risks has made sustainability and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) initiatives essential.
While both frameworks focus on promoting responsible practices, a key distinction lies in the fact that ESG involves a systematic evaluation of sustainability using benchmarks and metrics.
So, let’s learn about ESG vs Sustainability. What are the differences, and why do they matter?
ESG puts significant importance on investing or responsible investing, as it establishes a set of standards by socially conscious investors. Sustainability in business means incorporating sustainable business practices.
It underlines their role in shaping ethical and sustainable business strategies.
In recent years, Australian businesses have increasingly recognised the importance of integrating ESG and sustainable principles into their operations. It helps mitigate risks, enhance long-term resilience, and align with global sustainability goals.
What is Sustainability?
Sustainability means running a business that takes care of our world now without causing problems for the people who will come after us. There are three main parts to sustainability:
Environmental Sustainability: This part is about not hurting the environment. It involves using less energy, creating less pollution, and not wasting natural resources.
Social Sustainability: This part is about treating people fairly. It includes ensuring that everyone in the workplace is safe and treated well. It’s also about being fair to different kinds of people and getting involved in the community.
Economic Sustainability: This part is about ensuring the business can keep making money for a long time. It involves being responsible with money, creating value, and using resources wisely.
Corporate sustainability is when businesses try to be good for the environment, treat people right, and make money.
Businesses can be successful and helpful to everyone in the long run by improving how people are treated at work, respecting human rights, and not wasting resources.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Sustainability

Biodiversity:
- Biodiversity considers the variety of plants and animal species in the environment.
- Safeguarding biodiversity is critical for sustaining ecosystems’ natural balance.
Sustainable Development:
- Sustainable development ensures meeting present needs without compromising the well-being of future generations.
- Striking economic, social, and environmental balance is vital for sustainable business practices.
Supply Chain:
- A supply chain comprises the network of organisations, people, and activities involved in creating and delivering products or services.
- Integrating sustainable practices into supply chains is essential for minimising environmental impact and fostering ethical business conduct.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR):
- CSR entails initiatives taken to ensure a company operates ethically and sustainably.
- Examples: CSR efforts include charity work, clean-ups, and community contributions.
Sustainable Investing:
- Sustainable investing involves investors choosing companies with robust ESG performance and sustainable business practices.
- Investors prioritise companies demonstrating a commitment to ethical and sustainable principles.
These key sustainability terms are vital for anyone aiming to implement environmentally and socially responsible practices within their business operations.
It includes things like advanced sensors, computer programs that learn, and real-time monitoring. With these tools, companies can use energy in the best way, cutting down on waste and saving money.
Being more efficient not only helps businesses make more profit but also makes their way of working more sustainable and strong for the future.
What is ESG?
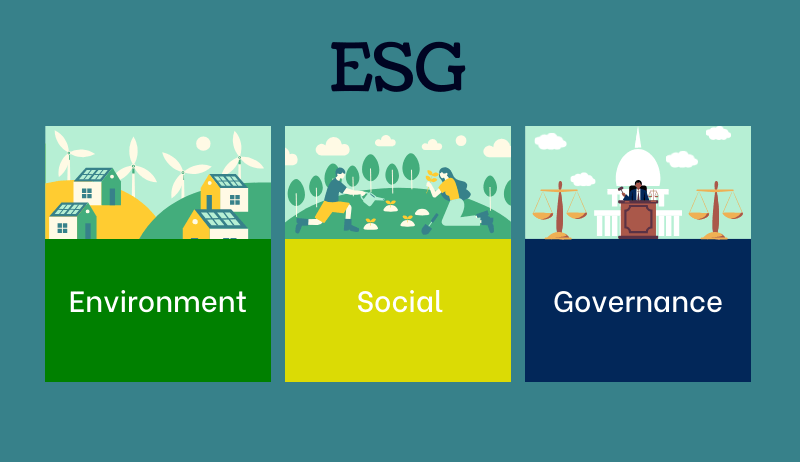
ESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance. It’s like a checklist to see how well a company does with the environment and people and profit by taking care of these elements.
ESG aims to help people like investors. Investors use ESG to decide if they want to invest in a company. The three parts of ESG are:
Environmental: This looks at how a company impacts the environment. It checks pollution, energy use, and how they handle waste.
Social: This checks how a company treats its people and the community. It looks at how workers are treated, diversity, and how the company acts in the community.
Governance: This looks at how a company is managed. It checks if the company is fair and ethical in its decisions, like having a diverse board, fair pay, and following the rules.
Doing well in ESG can be suitable for a company in different ways, like making more money, having a better reputation, and avoiding problems with rules.
More and more, companies are being rated on their ESG, and they share this information so that everyone knows how they are doing.
In recent years, people care more about companies that are good for society and the environment, making ESG more crucial than ever.
Key Terms ESG
Comprehending various terms, metrics, and frameworks is crucial to making ESG reports properly. These terms establish a shared language and criteria, enabling you and your investors to assess the impact on the environment, society, and corporate governance.
Here are some significant terms that merit familiarity:
ESG Factors:
- These encompass the environmental, social, and governance elements considered in ESG investing and reporting.
- Examples: Climate change, human rights, and executive compensation.
ESG Metrics:
- Also referred to as ESG data, these are pivotal performance indicators used to evaluate your ESG performance.
- Examples: Greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, waste management, and diversity and inclusion.
Frameworks:
- These offer a standardised approach to assess your ESG performance.
- Examples: Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), and Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB).
ESG Ratings:
- ESG scores evaluate ESG factors and frameworks your investors and stakeholders utilise to assess your company.
ESG Audits:
- These assessments are conducted internally or externally to evaluate your ESG performance and pinpoint areas for improvement.
ESG Risks:
- These refer to potential risks from your ESG performance, encompassing issues like reputational damage, regulatory fines, and reduced investor interest.
ESG Reporting:
- This involves disclosing your environmental, social, and governance performance to stakeholders, including investors, customers, employees, and regulators.
- In your ESG and sustainability report, include information on ESG factors and metrics, such as energy use, diversity and inclusion, and executive compensation, to enable stakeholders to assess your ESG performance effectively.
ESG vs Sustainability, What are the Differences Between ESG and Sustainability

Distinguishing between ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) and sustainability reveals their interconnected yet distinct nature.
Both concepts revolve around environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices. However, the difference lies in their scopes and applications.
ESG serves as a structured set of criteria to assess a company’s environmental, social, and governance performance.
It functions as a standardised framework, providing investors and stakeholders with a systematic way to gauge a company’s societal and environmental impact and corporate governance practices.
In contrast, sustainability is broader and encompasses principles that advocate for responsible and ethical business practices. It considers the relationship between environmental, social, and economic factors.
The primary distinction emerges in the utilisation of these concepts. ESG is a specific tool for measuring and evaluating a company’s performance. It focuses on carbon emissions, diversity and inclusion, and executive compensation.
On the other hand, sustainability is a comprehensive principle that spans various responsible business practices. It includes supply chain management, stakeholder engagement, and community development.
While ESG provides a targeted assessment tool, sustainability is a holistic framework for promoting responsible and ethical business conduct.
Both play crucial roles in shaping corporate behaviour. ESG offers specific metrics for evaluation and sustainability, guiding a company’s overarching commitment to ethical practices across diverse operations.
Why do Sustainability and ESG Matter for Australian Businesses?
Sustainability and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) considerations are increasingly vital for Australian businesses due to several compelling reasons:
Global Expectations and Trends:
The global business landscape is evolving, emphasising ethical and sustainable practices. International stakeholders, including consumers, investors, and partners, increasingly expect businesses to align with environmental and social responsibility standards.
Australian companies need to meet these expectations to remain competitive on the global stage.
Risk Mitigation:
Sustainability and ESG practices help mitigate risks associated with climate change, social issues, and governance shortcomings.
As climate-related risks become more pronounced, businesses proactively addressing these concerns are better equipped to navigate regulatory changes, supply chain disruptions, and other potential challenges.
Investor Preferences:
Both domestic and international investors are showing a heightened interest in companies with strong sustainability and ESG performance.
Many funds and institutional investors incorporate ESG criteria into their decision-making processes, and businesses that align with these principles are more likely to attract investment.
Social Licence to Operate:
Australian businesses rely on the support of local communities and stakeholders.
Demonstrating a commitment to sustainable and responsible practices enhances a company’s social licence, fostering positive community relationships and reducing the risk of reputational damage.
Regulatory Compliance:
The Australian regulatory landscape is evolving to include stricter environmental and social standards.
Following sustainability and ESG practices ensures that businesses are compliant with existing regulations and better positioned to adapt to future changes in the legal and regulatory environment.
Brand Reputation and Customer Loyalty:
Consumers increasingly make purchasing decisions based on a company’s ethical and sustainability practices.
Businesses prioritising sustainability and ESG considerations build a positive brand reputation, foster customer loyalty, and tap into a growing market of environmentally and socially conscious consumers.
Employee Engagement and Attraction:
Final Thought about ESG and Sustainability
Incorporating sustainability and ESG practices is not just about meeting ethical standards. It is a strategic imperative for Australian businesses to remain competitive, attract investment, mitigate risks, and build a positive and sustainable future.
Get a free solar quote from Cyanergy to keep up with your sustainable goals!